You might be familiar with shift-left testing, an approach that emphasizes testing earlier in the development lifecycle to identify issues as soon as possible. It is a strategy that almost every organization is trying to adopt these days. For good reason, too, as this approach significantly reduces costs and improves quality.
However, modern software systems are more complex with the introduction of distributed systems, microservices, cloud-native deployments, third-party integrations, and real-time user interactions. The challenges introduced by these newer technologies cannot always be fully validated before production. Shift-right testing comes to the rescue at this point.
| Key Takeaways: |
|---|
|
In this article, we will explore what shift-right testing is, why it matters, how it differs from traditional testing approaches, its key techniques, benefits, challenges, and how teams can successfully adopt it.
What is Shift-Right Testing?
Shift-right testing is a testing approach focusing on observability, monitoring, experimentation, and validation in post-production environments. It emphasizes understanding how applications behave under real-world scenarios and how actual users interact with them.
Shift-right testing tests the system behavior in reality (post-release) to continuously monitor and improve it.
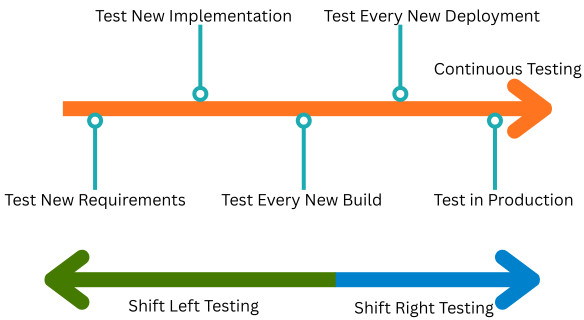
- Shift-right testing is a DevOps-driven approach.
- It tests software after its deployment in the production environment.
- It ensures real-world performance, reliability, and user experience for the deployed application.
- Shift-right testing focuses on monitoring production behavior, gathering end-user feedback, and validating system resilience and robustness under actual conditions.
Why “Shift-Right”?
Shift-right testing is done on the right side of the software delivery timeline, after development, staging, and pre-production, into deployed environments. Hence the term “shift-right”.
It is important that shift-right testing does not replace shift-left testing. Instead, it complements it. When combined, shift-left and shift-right testing approaches form a continuous testing loop that spans the entire software lifecycle. (Refer to the figure above)
Why Shift-Right Testing Is Necessary Today?
In today’s complex software environment, it is necessary to validate software applications in live, real-world conditions to ensure high performance, reliability, and user engagement. Shift-right testing achieves this as it bridges the gap between development, QA, and operations to ensure high reliability of applications.
Shift-right testing helps teams gain immediate user feedback, detect performance bottlenecks, enhance security against live threats, and improve system resilience. For organizations, moving beyond pre-deployment testing ensures that applications are not only functional but also secure and high-performing under actual user load.
- Real Users Behave Differently Than Test Scripts: No matter how extensive and comprehensive your test cases are, they cannot fully predict the unexpected user flows, edge cases arising from real usage patterns, and cultural, geographic, or device-specific behavior.
Shift-right testing helps teams to learn directly from real user interactions. It provides insights into how users actually interact with the application, enabling data-driven improvements that staging environments cannot replicate.
- Production Environments Are Unique: Production environments differ from test or staging environments, and it is hard to replicate real traffic volumes, network latency, third-party service instability, data size, and variability. Issues like memory leaks, race conditions, performance degradation, or data inconsistencies appear only in production.
- Faster Release Cycles Demand Continuous Validation: Modern software applications are released frequently with CI/CD, DevOps, and DevSecOps practices. Traditional “test-before-release” models cannot keep up with these fast-paced release cycles.
- Continuous Monitoring and Security: Shift-right testing enables real-time threat detection and security compliance monitoring in live environments where threats are most prevalent.
- Improved Resilience: Shift-right testing uses methods such as chaos engineering (e.g., simulating server failures) to ensure systems can withstand unexpected, real-world failures.
Shift-Left vs Shift-Right Testing
The following table summarizes the key differences between shift-left and shift-right testing approaches:
| Aspect | Shift-Left Testing | Shift-Right Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Timing | Before production, in the early stages of development (requirements, design, coding) | After production in the deployed environment |
| Focus | Defect prevention and early detection | Behavioral insight and optimization with real-world validation, performance monitoring, and user experience enhancement |
| Emphasis | Proactive quality assurance and code-level issues | Reactive monitoring, operational quality, and user behavior insights |
| Data | Uses synthetic / test data | Testing is performed with real user data |
| Goal | Performed with the intention of catching bugs early | Aims to improve reliability, UX, and performance |
| Testing Techniques | Unit, integration, automation, static code analysis, and code reviews | Monitoring, A/B testing, chaos engineering, feature toggles, and user feedback analysis |
| Cost of Fixing Bugs | Lower – bugs are caught when they are cheapest and easiest to fix | Higher – issues found in production require faster remediation and can impact users |
Both approaches are necessary. Shift-left reduces risk; shift-right manages reality.
Core Principles of Shift-Right Testing
- Testing in Production: Shift-right testing moves testing beyond pre-release testing to validate how software behaves under actual traffic and user behavior.
- Continuous Monitoring and Observability: It uses real-time data to detect issues such as performance bottlenecks or unexpected bugs immediately after deployment.
- User-Centric Feedback: As a result of shift-right testing, direct, real-world feedback is gathered from users to drive enhancements and new features, ensuring the application meets user needs.
- Controlled Experimentation (Canary/AB Testing): Shift-right testing is sometimes performed under controlled experimentation by releasing new features to a small subset of users first to test stability and performance. This reduces the risk before a full feature rollout.
- Resilience and Fault Injection: Shift-right testing proactively tests system robustness by simulating failures (e.g., Chaos Engineering) in production to ensure high availability.
- Fast Feedback Loops: They use data to immediately inform development teams, enabling rapid iterations and shorter time-to-market for fixes.
Key Techniques in Shift-Right Testing
1. Canary Releases
In a canary release, a new feature or a version of the application is released to a small subset of users before it is fully deployed. With this controlled release, you can identify potential issues and also monitor its behavior closely before it affects the entire user base.
If there are any issues, the release is rolled back for fixing. The canary release technique helps to test the stability of the application before a full launch.
2. A/B Testing
A/B testing technique compares two versions (A and B) of the same feature to determine which performs better. When two different versions of the same feature or component are exposed to different user segments, you can gather valuable insights into user behavior and preferences. This helps improve user experience, increase user engagement, and optimize business outcomes.
3. Feature Flags and Toggles
The feature flag and toggle technique allows developers to enable/disable features in production without deploying new code. This flexible technique can help to test new functionalities in a live environment and roll back changes quickly if necessary.
With feature flags and toggles, experimentation becomes safer and more controlled.
4. Chaos Engineering
Chaos Engineering is a technique of intentionally introducing failures (e.g., shutting down services or injecting latency) into a production system to validate system resilience. By simulating unexpected failures and faults, teams can improve the system’s robustness and identify its weak points.
Chaos engineering technique is popular with companies like Netflix and ensures systems can withstand real-world challenges.
5. Production Monitoring and Logging
Monitoring is the foundation of shift-right testing. The various parameters monitored during shift-right testing include application performance (latency, throughput), error rates, resource usage (CPU, memory), and business metrics (conversion rates, drop-offs). Logs and metrics help teams identify issues before users complain.
6. Real User Monitoring (RUM)
When users interact with the application, the RUM technique captures data directly from users’ browsers or devices, including page load times, JavaScript errors, device and browser types, and geographic performance variations.
This continuous monitoring provides insights into performance issues, user experience bottlenecks, and other critical metrics that synthetic tests cannot.
Benefits of Shift-Right Testing
- Improved Reliability: Shift-right testing identifies performance bottlenecks, hidden defects, and bugs in the live environment. Developers can fix these issues quickly, improve fault tolerance, and reduce downtime.
- Better User Experience: This testing technique focuses on actual user experience in a live environment that enables faster pages, smoother workflows, and reduced friction. It provides valuable insights that pre-production environments cannot simulate.
- Continuous Feedback Loops: Shift-right testing facilitates immediate user feedback on new features, ensuring alignment with user expectations and allowing for rapid iterations.
- Reduced Risk of Large Failures: Shift-right testing techniques like chaos engineering build a more robust system capable of withstanding unexpected failures gracefully. The risk of major outages, reputational damage, and costly rollbacks is reduced because of incremental rollouts and monitoring.
- Business-Driven Quality: Production monitoring during shift-right testing provides data-driven insights and aligns quality with revenue impact, retention metrics, and customer satisfaction.
Challenges of Shift-Right Testing
- Fear of Testing in Production: Many teams may hesitate to test production systems because of their concerns regarding user impact, data privacy, and brand reputation, though shift-right testing emphasizes safe, controlled experiments.
- Tooling and Observability Gaps: Without proper testing and monitoring tools, teams may find it challenging to interpret large amounts of data, act on insights, and correlate events across services.
- Cultural Resistance: This technique needs a mindset shift from “release and forget” to “release and learn”. This shift can face cultural resistance from teams as testing moves from siloed QA to shared ownership.
- Data Noise: Production data obtained from shift-right testing can be overwhelming. In such a case, it is challenging to define meaningful metrics, filter noise, and focus on actionable signals.
- Feature Rollback: If any issues are observed in production during shift-right testing, the feature should be quickly rolled back. For this purpose, a robust rollback mechanism should be in place, consisting of sophisticated deployment pipelines, comprehensive monitoring systems, and well-defined incident response procedures that can execute rapidly when problems arise.
Best Practices for Adopting Shift-Right Testing
- Start Small: Begin your shift-right testing with small steps like monitoring key endpoints, canary releases for low-risk features, and basic user metrics. When these steps are mastered, then expand the testing.
- Invest in Observability: Implement strong observability. Ensure clear dashboards, an alerting system tied to user impact, and correlation across logs, traces, and metrics.
- Integrate QA into Production Insights: Ensure QA teams switch from their gatekeeper role to quality strategists by analyzing production issues, designing experiments, and using real-world data to improve test coverage.
- Use Automation for Safety: Use automation for rolling back features, issuing alerts, and implementing health checkups to reduce risk and increase confidence in production experimentation.
- Align with Business Goals: Track metrics such as conversion rates, error impact on revenue, and performance vs retention that matter most.
Shift-Right Testing and the Future of QA
- AI-Driven Autonomous Testing: AI will be used to generate, execute, and maintain test scripts, as well as predict potential failures based on historical data.
- Self-Healing Tests: Test scripts will be automatically updated when the application UI changes, significantly reducing maintenance efforts.
- QAOps (DevTestOps): QA activities will be fully integrated into DevOps pipelines, treating testing as code and enabling real-time validation with every commit.
- Shift from “Bug Hunter” to “Quality Engineer”: QA professional is becoming a strategist who uses data to improve product quality, user experience, and stability.
- Democratization using Low-Code/No-Code: This will allow non-technical teams to contribute to test creation.
Conclusion
Shift-right testing technique is a fundamental shift in how teams think about quality. It agrees with a simple truth: no test environment can fully replicate production. By testing in production using real-world data, continuous monitoring, and safe experimentation, teams can deliver more reliable, resilient, and user-centric software.
Working along with traditional testing, shift-right testing ensures quality does not end at deployment but continues to evolve with every user interaction. Pair it with shift-left testing, and you have a foolproof strategy to ensure high quality.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can shift-right testing replace traditional pre-production testing?
No, shift-right testing is not a replacement for early-stage testing. Instead, it complements traditional testing by providing comprehensive quality assurance throughout the entire software lifecycle.
2. Which issues appear only when shifting right?
Shift-right testing often identifies performance bottlenecks, configuration problems, integration issues, and unexpected user behavior. In general, issues that are difficult to reveal in test environments due to their reliance on real traffic, data, and infrastructure are identified through shift-right testing.
3. Can small teams or startups adopt shift-right testing?
Absolutely. In fact, many smaller teams find it advantageous to start with basic system monitoring and canary releases. Shift-right testing doesn’t require any enterprise-level resources; it only requires thoughtful scoping, controlled exposure, and clear goals for what you want to achieve after deployment.
4. Which is better: shift-left or shift-right?
Actually, neither is “better.” Both strategies have their own objectives, serve different purposes, and address different risks. While shift-left saves on defect costs by catching issues early, shift-right validates real-world behavior in production. Both strategies, when adopted simultaneously, provide comprehensive quality assurance.
5. When adopted simultaneously, what should be the share of each?
In the entire SDLC, the typical distribution of shift-left and shift-right testing is: 70-80% of testing effort occurs left (development, CI/CD, staging) to identify issues early when they’re cheap to fix. 20-30% focuses right (production monitoring, synthetic testing, real user monitoring, observability) to validate real-world behavior. However, the exact share percentage will depend on application risk, regulatory requirements, and business priorities.
