If you’ve been in the QA field for a while, you’ve already seen multiple trends come and go. But through all of them, one message seems to get clearer and clearer – software testing is no longer just an afterthought.
Shift everywhere testing is one such concept that helps assimilate software testing into various aspects of the software development process. Initially, it was shift-left testing that was considered the modern way to do QA, then came shift-right, and now, we are testing everywhere, meaning, at every stage. Quality checks slip in quietly during design, coding, and even planning talks. Work changes slowly as habits adapt behind the scenes.
| Key Takeaways: |
|---|
|
Let’s understand more about shift everywhere testing; what it means and how it can help improve your QA process.
Shift Everywhere Testing as a Holistic Testing Strategy
At its core, shift everywhere testing is a holistic testing strategy, even though it often shows up as a mindset shift. Instead of treating testing as a separate activity, it connects people, processes, tools, feedback, and learning into one continuous flow.
Nothing stands in isolation. Tests, monitoring data, user feedback, and incidents all act as quality signals. An issue in production? Not just a failure but an opportunity to learn. Flaky tests appear messy at first glance yet hint at hidden shifts beneath.
This broader view shifts the team’s mindset on quality. Curiosity takes over where fear once lived. Instead of thinking, “Part of my code works”, the question becomes, “Does the system work?”
Shift Left vs. Shift Right: A Quick Recap
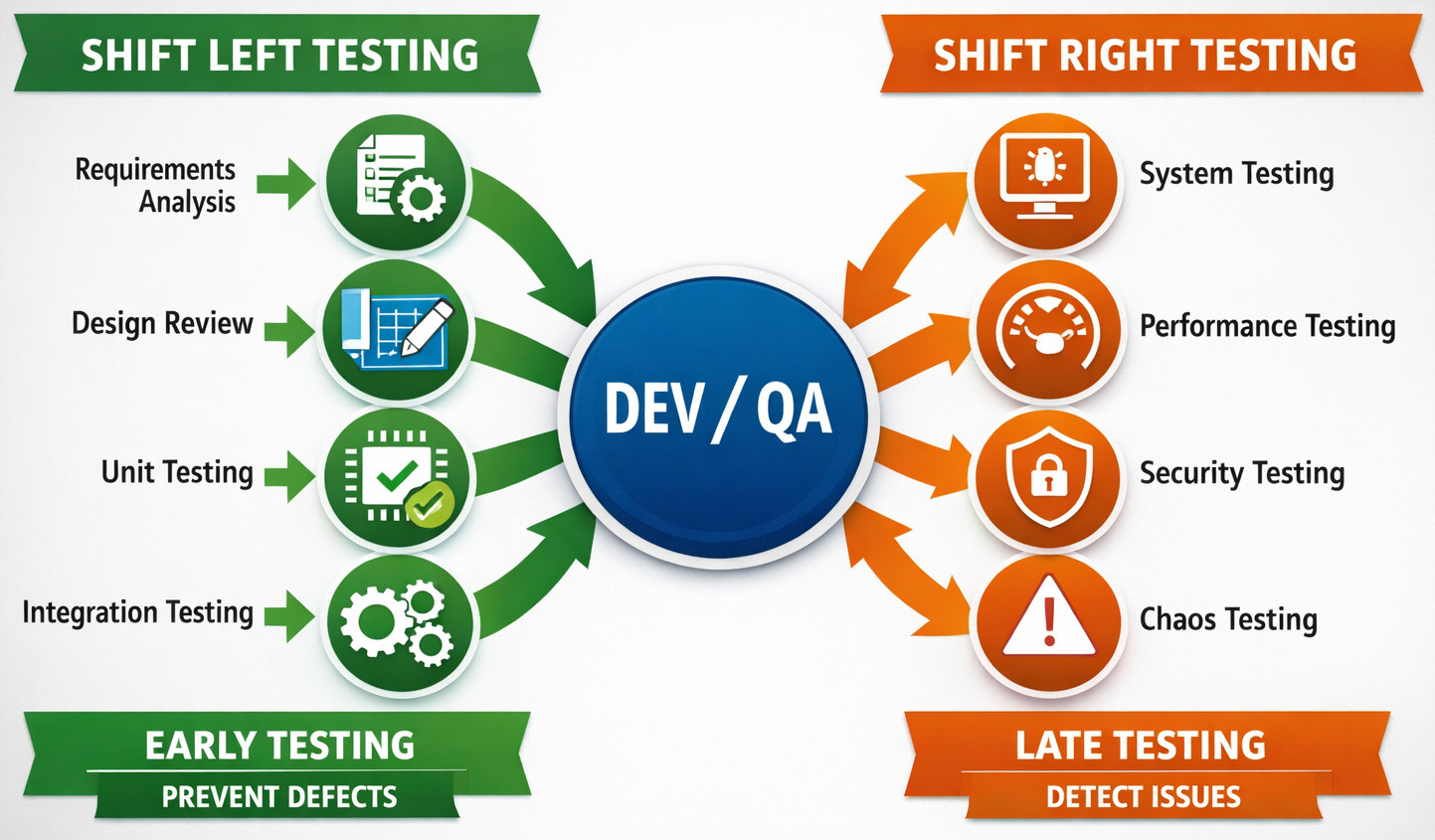
Firstly, ‘shifting’ in this context simply means when in the timeline of building a product you perform your testing. If you imagine a project timeline as a line from left to right (Plan -> Build -> Launch), you are moving your testing focus toward one of those ends.
Shift-Left Testing
Shift-left testing means that we are testing early in the development cycle. Over here, testers don’t wait for the product to be finished. Instead, you’ll see parallel testing happening; test cases being written alongside software development. This is a great way to incorporate testing early into the lifecycle, as it is way less expensive to fix bugs at this stage. Read more about shift-left testing over here: What is Shift-Left Testing?
Think of shift-left testing as a way to “test early and often”.
Shift-Right Testing
Over here, we shift to the right side of the timeline, that is, after the software has been launched to the users. This brings out various interesting insights, like user experience, performance, etc., that you can simply not gauge in shift-left testing.
Think of shift-right testing as a way to “test in the real world”.
Shift Left vs. Shift Right
| Feature | Shift-Left | Shift-Right |
|---|---|---|
| When? | During design and development. | After deployment/launch. |
| Focus | Prevention and correctness. | Performance and user experience. |
| Environment | Staging/developer’s computer. | Production (the real world). |
| Philosophy | “Don’t build it wrong”. | “Make sure it stays right”. |
The Problem With Testing
For a long time, software testing followed a neat, predictable flow.
Start by creating the software. When finished, run tests on it. Where things fail, fix the issue and make the software work.
Back then, this process made sense, systems stayed simpler, and releases came slower. Now, modern software moves faster, though, while testing often lags behind.
Software Has Become Messy (And That’s Normal)
- Microservices constantly talk to other services.
- Third-party APIs can fail without warning.
- Cloud environments scale up and down dynamically.
- AI models evolve and change behavior over time.
- Releases happen daily, sometimes multiple times a day.
In this kind of environment, testing once at the end is no longer enough.
Where Traditional Testing Starts to Fall Apart
- Testing happens too late, so defects escape into production
- Feedback loops are slow, making fixes expensive and frustrating
- QA teams become bottlenecks, overwhelmed by last-minute validation
- Developers disengage from testing, seeing it as someone else’s responsibility
What you get is reduced trust in updates – not simply extra bugs.
The Real Issue: Testing Is Treated as a Phase
Right now, the issue isn’t about what people know or what they use. What matters most is where testing sits in the process.
Traditional models treat testing as a separate step instead of a continuous activity. When requirements shift fast, those traditional approaches stumble – built on steady specs, smooth workflows, predictable outcomes, conditions live production seldom meets.
A steady flow of updates pushes tests to keep pace – each step demanding quick turns.
Why Shift-Left and Shift-Right Aren’t Enough?
- Shift-Left pushed testing earlier in the lifecycle. Because of this change, developers began crafting small tests early. QA stepped into planning talks before coding kicked off. Catching defects faster became normal across teams. Things improved because of it.
- Shift-Right focuses on validating software in production. Monitoring, feature flags, and user feedback reveal how systems behave in real conditions. This approach brings its own kind of clarity.
Testing early or testing late – that’s what both methods really focus on. Yet each keeps seeing quality as just another step, something tucked away instead of lived every day. Balance begins when sides stop mattering. Instead of labels, something steady emerges. Not left or right.
We need testing everywhere – in planning, in code, in pipelines, and in production. Quality grows through steady monitoring. Progress comes from tweaks made real, step by step.
Shift Everywhere Testing: A New Way of Thinking
Shift everywhere testing is an approach where testing and quality checks happen across the entire software lifecycle. It is not a separate phase, but a continuous activity.
From the first plans and designs of a project, testing takes shape. As work moves forward, it lives inside development CI/CD pipelines. And it extends into production through monitoring and user feedback. Testing also emerges when systems scale, integrations change, or incidents occur.
Starting right up front and stretching all the way through, shift everywhere testing naturally combines shift-left and shift-right practices into one continuous flow. Instead of passing quality around like a baton, teams hold onto it together, shaping it constantly as they go.
Continuous Testing as the Backbone
People dive into shift everywhere testing, yet skip past continuous testing at their peril. But continuous testing is not just automation. Mentioning the first pulls the second right into view. Yet testing nonstop isn’t only about automation doing checks. Many get that wrong.
- A broken unit test
- A slow API response
- A spike in errors after deployment
- A broken integration
- A data mismatch
If you notice, every one of these is a test. Thus, by integrating continuous testing into the lifecycle, you can elevate your shift everywhere testing process.
Common Misunderstandings About Shift Everywhere Testing
- Shift everywhere testing does not mean testing everything, all the time, manually. It’d slow teams down. Smarter feedback comes from choosing tests that fit the situation, timed well. Feedback improves when effort matches need.
- It also does not require a complete overhaul of tools. Chances are, most teams own everything required. Shifting happens in usage, how testing software gets applied, how fast and efficient responses form when alerts pop up.
- Shift everywhere testing does not replace QA. Actually, it gives QA more weight. People in QA get nearer to key choices, guiding teams on where risks lie, what needs validating, and how good things really are, continuously across the lifecycle.
- Shift everywhere testing does not remove structure. Swapping rigid testing phases with flexible, continuous learning keeps things moving, just without the stiffness.
And finally, this isn’t something you “roll out” in a sprint or two. It’s a mindset that develops gradually as teams learn to trust shared ownership of quality.
How Teams Execute Shift Everywhere Testing – An Overview
- It starts early, during planning and design. Questions guide the path, not just tasks. Developers weigh edge cases long before development begins. Acceptance rules grow clearer because testers speak up first. Testing here is mostly about asking the right questions.
- During development, developers and QAs work closer than before. Unit and integration tests provide fast feedback. Issues pop up early, caught while changes are fresh. In these moments, shift-left testing quietly does its job.
- When code travels along pipelines, automated checks, validations, and reviews work as constant quality signals.
- In production, monitoring tools and user feedback shape awareness of actual performance and weak spots. That’s shift-right showing up.
Eventually, testing no longer seems like just a step. It becomes part of how things progress, woven into the rhythm instead of sitting outside it. What once felt temporary now lingers, quietly shaping each moment that follows.
Quality Is No Longer a Phase
If there’s one idea to take away, it’s this: Quality is no longer something you check. It’s something you build, observe, and improve constantly. Testing everywhere means learning through mistakes. Not chasing flawless results. When teams learn this, they can better adapt to the changing nature of software development and implement effective checks and balances.
FAQs
Is shift everywhere testing just another name for automation?
No, not really. Automation is important, but shift everywhere testing is bigger than that. It’s about continuous feedback across the lifecycle. Some of that feedback comes from automated tests, but a lot of it comes from monitoring, user behavior, collaboration, and learning from failures.
What role does observability play in shift everywhere testing?
Observability is critical. Logs, metrics, and traces act like tests running in production. They help teams understand how systems behave in real-world conditions and provide rapid feedback when something goes wrong.
How can a team start adopting shift everywhere testing?
Always start small. Improve test feedback in CI/CD, involve QA earlier in discussions, and pay more attention to production signals. Over time, encourage shared ownership of quality and learning across roles. The mindset matters more than the tools.
