The Test Data Management (TDM) industry is expanding rapidly; the global market is expected to grow from its current 2023 valuation of US$1.3 billion to an estimated US$2.7 billion by 2030. (source)
In today’s fast-paced development cycles, there are no secure applications without sound data handling. TDM has emerged as a cornerstone of helping software teams fulfill requirements for speed, quality, and regulatory compliance. Whether you are building large-scale enterprise systems, working on your QA teams, or doing some sort of DevOps, a good understanding of TDM is important to have in order to promote smooth, safe, and on-time releases.
In this blog, we will dissect TDM: what it is, why it is important, how it is part of the Agile-DevOps story, and the ideal strategies to maximize coverage and effectiveness.
Understanding Test Data Management (TDM)
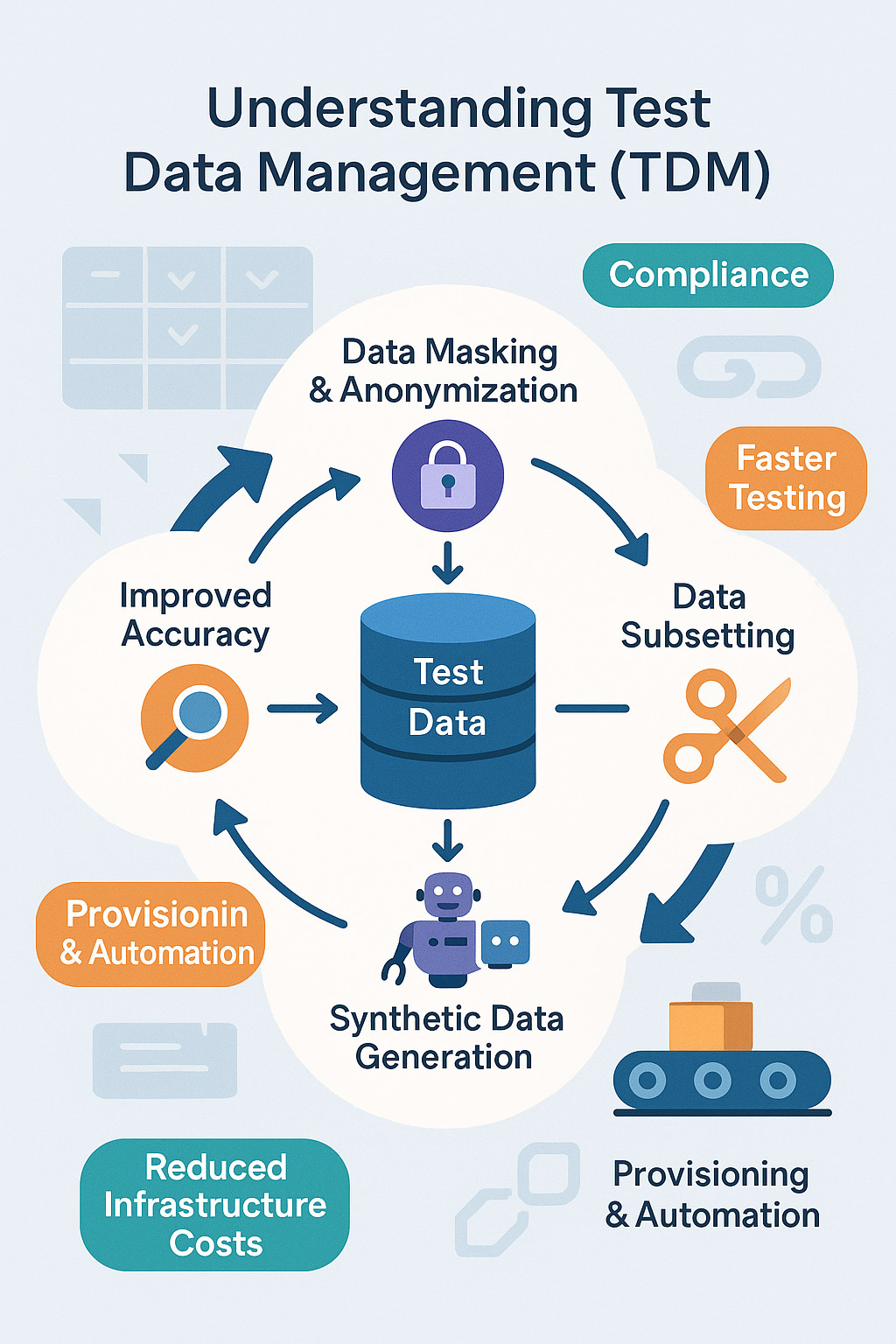
The main objective of TDM, is to ensure that the right test data is available and accessible when needed. This includes creating and managing datasets for software teams that closely match actual production data without running the risk of sensitive information being exposed.The goal is to maintain 100% compliance with privacy laws.
Many teams used to develop test environments by just copying production databases. However, there are major problems associated with scalability and security in this strategy. TDM has evolved since then. Teams now use more intelligent techniques, such as data masking, subsetting, and synthetic data generation, rather than copying entire datasets. Another important factor is automation, which aids the provisioning of test data across development pipelines.
Why Does Software Testing Need TDM?
- Increased Accuracy and Test Coverage: When test data is properly managed, environments closely look like real-world systems. In the end, this keeps defects from making their way into production by enabling teams to confidently verify core functionality, edge cases, and performance scenarios.
- Smaller Release Schedules: Just-in-time data availability is supported by TDM. Teams can avoid data-waiting bottlenecks and maintain smooth Agile and DevOps workflows by provisioning test datasets as needed.
- Compliance Requirements: Even in test environments, regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS require careful data handling. By masking or anonymizing personally identifiable information (PII) prior to its use in testing, TDM contributes to privacy protection.
- Reduced Infrastructure Costs: Using data subsetting and virtualization, teams work with only the data they truly need – reducing storage and compute costs while keeping test cycles lean and efficient.
Key Components of TDM
- Data Discovery and Classification: Start by identifying sensitive data such as financial records or health information. Automated tools can scan fields and categorize them accordingly, laying the solid foundation for relevant masking or exclusion.
- Data Masking and Anonymization: Sensitive data are converted into safe, non-identifiable value using masking approaches such as substitution, nulling, shuffling or encryption. This can help data integrity and privacy without compromising on test accuracy.
- Data Subsetting: Instead of copying full databases, subsetting allows teams to extract only what’s needed for specific scenarios. This accelerates testing and reduces the burden on infrastructure.
- Synthetic Data Generation: If real-world data is not yet an option, or you don’t have the resources for enough edge cases, you can always safely simulate your own using synthetic data. It’s particularly useful in performance and negative testing, when it is important to control the test environment.
- Provisioning and Automation: Provisioning guarantees that the correct data is delivered to the proper environment at the appropriate time. TDM can be embedded in CI/CD pipelines using automation tools to enable self-service and continuous testing across teams.
Techniques Commonly Used in TDM
Static vs Dynamic Data Masking: Static masking changes data before it’s pushed into the test environment. Dynamic masking, on the other hand, masks data in real-time without changing the source.
Data Virtualization: Rather than replicating datasets, virtualization offers a virtual copy. This is best for rapidly spinning up ephemeral environments used in DevOps workflows.
Snapshotting and Bookmarking: Bookmarking lets testers save and respond to known data states, which is specially useful during automated regression or iterative testing cycles.
Major TDM Software in the Market
Ultimately, choosing the right TDM tool will depend on your tech stack, legal and privacy considerations, and how deeply you want to integrate it into your pipelines. Here are some tools you might have heard of:
- Delphix – Known for scalable data virtualization and masking.
- Informatica TDM – Offers features like synthetic data generation and deep profiling.
- Redgate Test Data Manager – Best for SQL Server environments; provides strong automation and masking tools.
- K2View – Provides micro-database-based data provisioning and strong self-service capabilities.
TDM in Agile and DevOps
Agile and DevOps teams depend strongly on constant, fast feedback. TDM supports these models by offering:
- On-demand test data for developers and QA.
- Automated data refreshes through CI/CD.
- Lightweight, ephemeral environments to support parallel testing.
- Data consistency across multiple test environments.
When test data flows as seamlessly as code, quality becomes easier to scale.
Best Practices for Implementing TDM
- Build a comprehensive strategy. Clearly define your goals, data types, and compliance demands before diving into TDM tools.
- Automate where possible and feasible. Embed TDM tasks such as masking and provisioning into your CI/CD pipelines where appropriate.
- Use synthetic data wisely. Especially when you need to replicate rare, intricate, or data-sensitive scenarios.
- Keep data quality high. Regularly profile and verify your datasets to avoid false positives or unreliable test results.
- Maintain traceability. Monitor when, how, and why test data changes. This is helpful and necessary for audits, debugging, and compliance reviews.
Conclusion
Test Data Management is a strategic catalyst for speed, compliance, and quality, and it goes far beyond a technical obligation. Teams can confidently deliver high-quality and secure software at scale by embracing modern TDM practices.
Faster releases, improved governance, and reduced defects are all advantages of investing in TDM, regardless of whether you’re handling legacy systems or developing next-generation applications. TDM’s importance will only increase as delivery schedules reduce and data privacy regulations become stricter.
