
You can not deny the vital role that test management tools have in the testing processes and activities. They help you immensely to organize and manage the process, from planning, execution, tracking, and finally reporting. The test management tools are more like a centralized repository where we can manage test plans, test cases, and test results. With these tools, we can improve collaboration between our team members.
Additionally, they streamline the workflow through integrations with other development and testing tools and help to improve overall project quality and delivery timelines. There are many test management tools available in the market.
Xray is one of the most commonly used tools. In this article, we will see its features, benefits, and associated challenges, as well as a preview to help you get started.
About XRay
Xray is a complete test management tool integrated with Jira. It is mainly designed to streamline and enhance the testing process across various project environments. It supports both manual and automated testing projects. Using Xray, the project teams can manage their test activities directly within Jira. You can create, organize, and execute test cases, linking them to requirements and defects for traceability. Your QA team can plan and execute test cycles and provide detailed reporting and analytics to monitor test coverage and progress.
One of Xray’s key features is its ability to create detailed test plans and manage test executions. Consider a software release that involves multiple testing cycles, including unit testing, integration testing, and user acceptance testing. With Xray, the test manager can create a comprehensive test plan outlining all the test cases, assign them to specific testers, and schedule their execution across different environments. During execution, testers can record their results, report defects, and provide feedback directly within the Xray interface.
Xray integration with Jira provides end-to-end traceability from requirements to test cases and defects. This promotes better alignment between testing efforts and project goals. Xray provides a user-friendly interface and features that can be customized based on different methodologies used by different projects.
Xray Products
Based on the requirements, Xray offers different products and features. Let us have a look into that.
- Xray Premium Onboarding: This is a specialized service offered by Xray with features like personalized training sessions, setup assistance, and best practices guidance.
- Xray Exploratory Testing: Xray supports exploratory testing, which is a hands-on, unscripted testing approach for discovering defects that may not be covered by predefined test cases. With this, you can document their exploratory sessions, capture real-time observations, and link findings to requirements and defects within Jira.
- Xray Enterprise: Xray Enterprise is designed for large-scale organizations with complex testing needs. It includes advanced features tailored to enterprise environments, such as enhanced performance, scalability, and security.
- Xray Test Management: Xray Test Management is the core functionality of the Xray suite, offering comprehensive tools for managing all aspects of the testing process. This includes creating, organizing, and executing test cases, managing test plans and test cycles, and tracking test results.
Benefits of Using Xray
Using Xray for test management offers several significant benefits. It has benefits for efficiency and effectiveness of the software development lifecycle. Here are some of the key benefits:
- Unified Platform: Xray is fully integrated within Jira, allowing you to manage testing activities alongside your project management tasks. This integration provides a seamless experience and ensures that testing is an integral part of the development process.
- Support for Manual and Automated Testing: Xray supports both manual and automated testing, allowing you to manage all their test cases in a single platform. Automated test results can be imported and managed within Xray, providing a unified view of all testing activities.
- Defect Management: Xray integrates with Jira’s defect tracking capabilities, enabling efficient management of defects. You can easily create and link defects to test cases, ensuring that issues are tracked and resolved promptly.
- Traceability: Xray ensures end-to-end traceability by linking requirements, test cases, and defects. This visibility helps you track the status of testing efforts and ensure that all requirements are adequately tested.
- Advanced Reporting and Analytics: Xray offers advanced reporting and analytics features, providing insights into test coverage, progress, and quality. Customizable dashboards and reports help stakeholders make informed decisions based on real-time data.
Challenges with Using Xray
While Xray offers numerous benefits as a test management tool, there are also some challenges associated with its use. Understanding these challenges would be better before you go for this tool.
- Licensing Costs: Xray licensing costs, especially for large teams or enterprise environments, can be significant. You should evaluate the cost-benefit ratio and ensure that the investment in Xray aligns with your budget and expected ROI.
- Additional Resources: Implementing and maintaining Xray might require additional resources, such as dedicated personnel for test management and server maintenance. This will add to the overall cost of the software.
- Customization Complexity: While Xray offers advanced reporting and analytics features, customizing reports to meet specific needs can be complex. You may need to invest time in learning how to create and modify reports effectively.
- Data Migration: Moving existing test cases and results from other test management tools to Xray can be challenging. You should carefully plan and execute data migration to avoid data loss or inconsistencies.
- Scalability Concerns: For very large projects with extensive test cases and executions, performance can sometimes be a concern. You may experience slower response times, especially in Jira Server or Data Center environments with high volumes of data.
- Customization: While customization is a strength, it can also be a challenge. Setting up custom workflows, fields, and integrations requires a good understanding of both Xray and Jira, which might be difficult for people without any prior experience.
Preview of Xray
Let’s see a quick demonstration of how we can create test cases and view the results of test execution using Xray.
View Xray Dashboard
Once you install Xray through Jira Marketplace, it will be listed in the Apps menu. We can see the Apps menu on the top header of Jira.
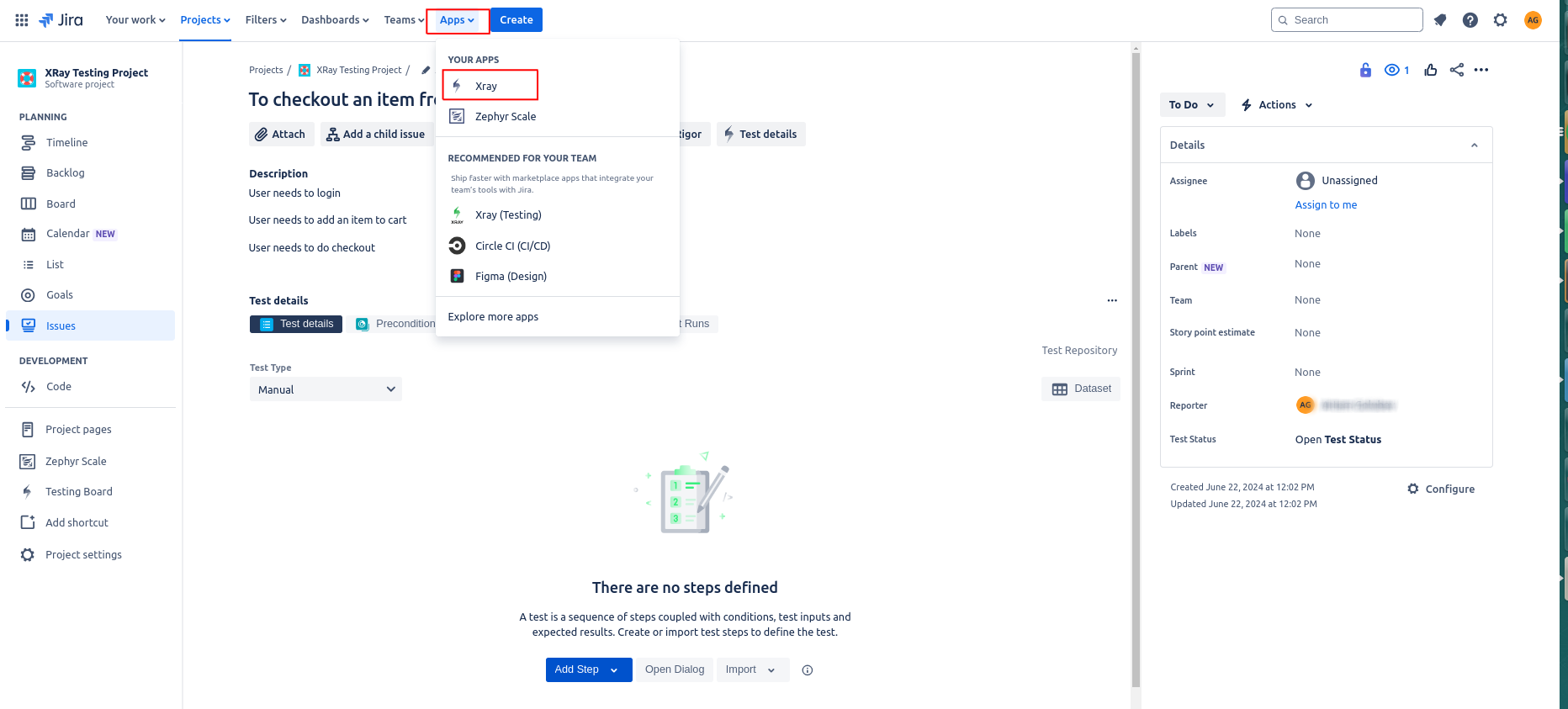
To view the Xray Dashboard, you need to click the Testing Board link on the left-hand side panel. The Xray Dashboard shows you all the test cases. Also, you can create a new folder to add test cases.
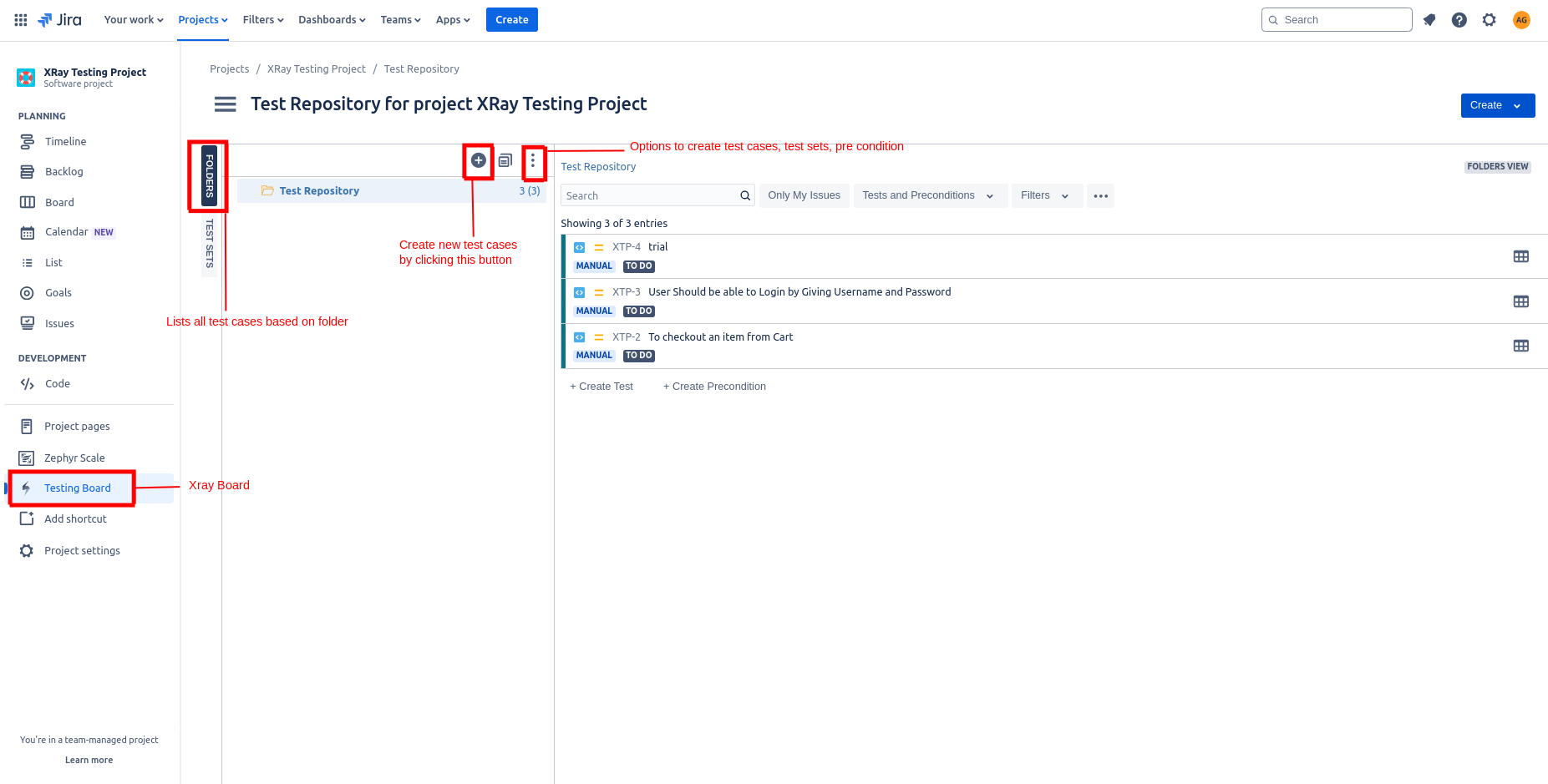
Create Test Case
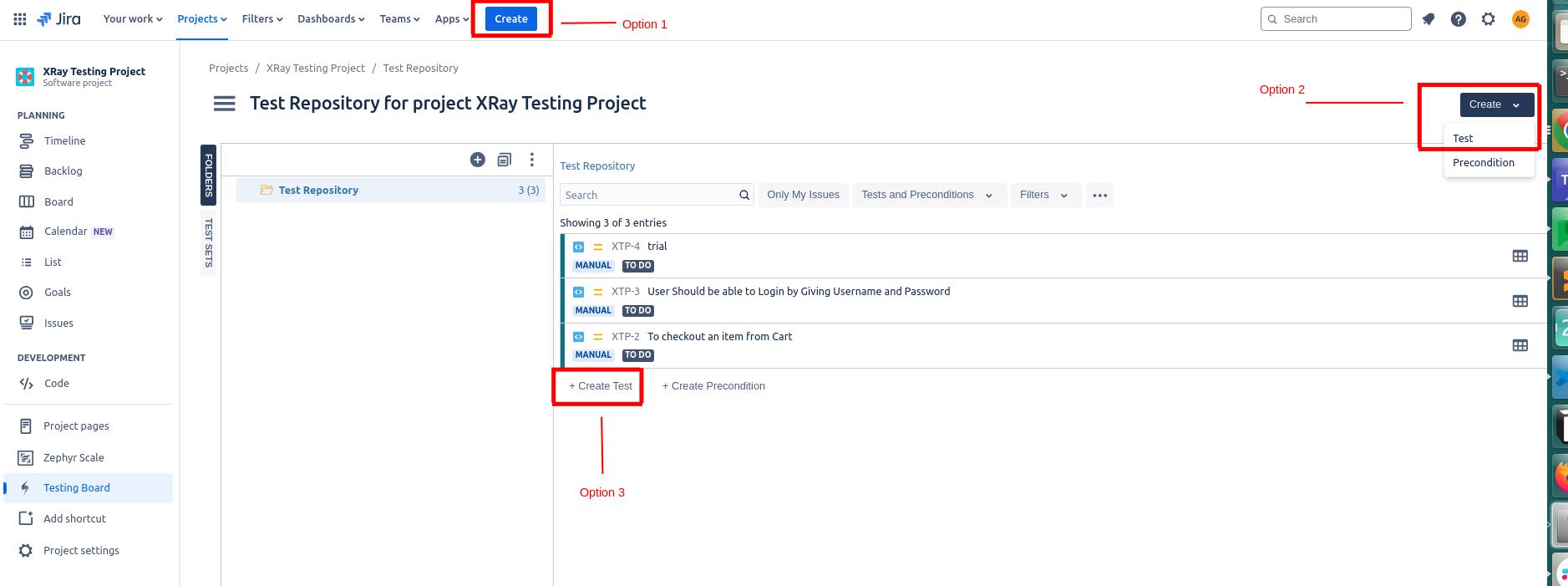
To create a new test case, you have three options; one is to click the Create on top of the screen or click the Create on the top-right side and select Test from the drop-down menu. The third option is to click the Create Test link below the test cases.
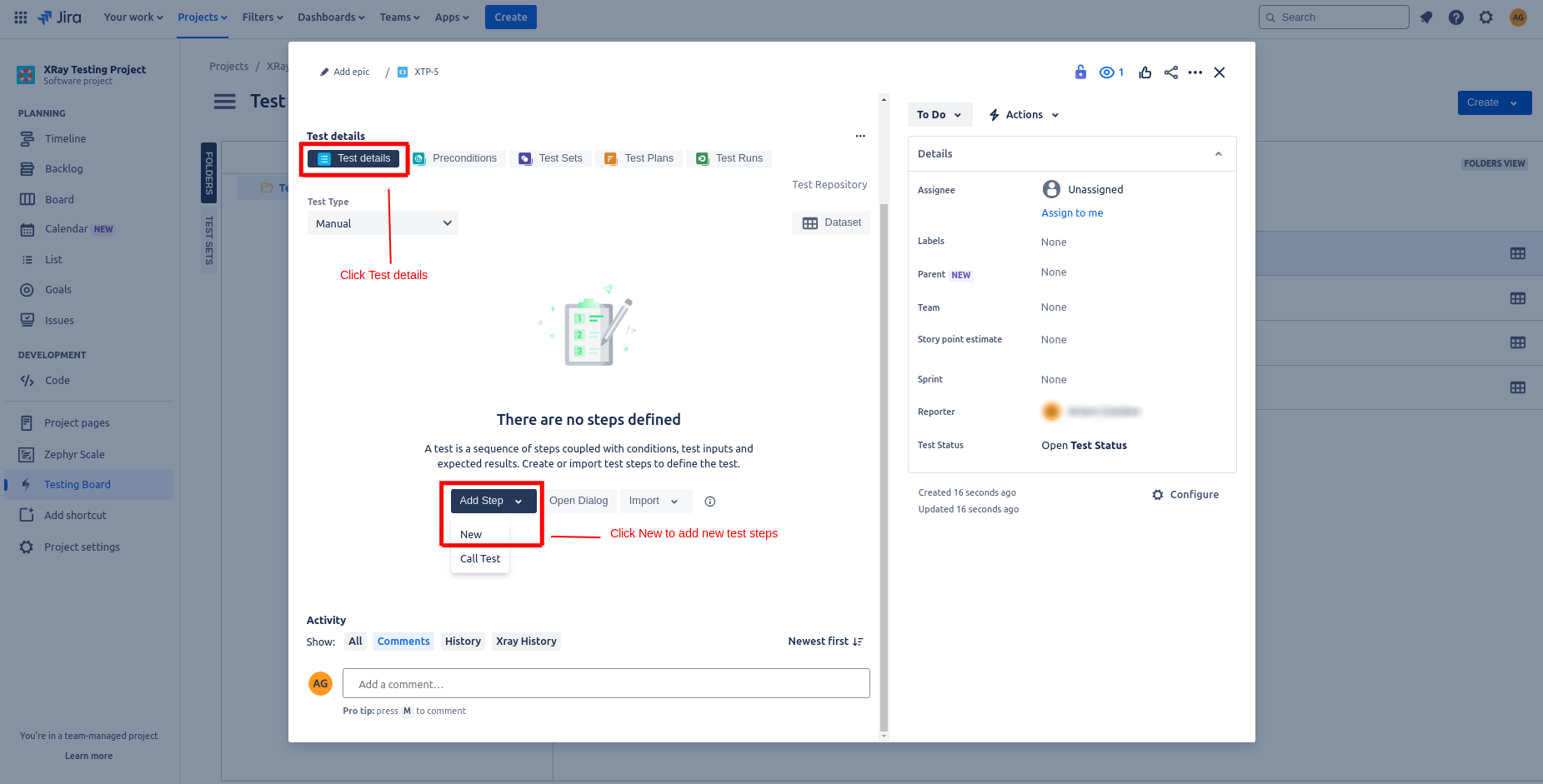
Add Test Steps
Once you create the test case, open it to see different X-ray options like adding Test Steps, Preconditions, Test Sets, Test Plans, and Test Runs. To add the test steps, click the Add Steps under the Test details.
Create Test Executions and Reports
From the Xray Board title, click the hamburger icon. It shows many options, such as creating test executions, test plans, and different types of reports.
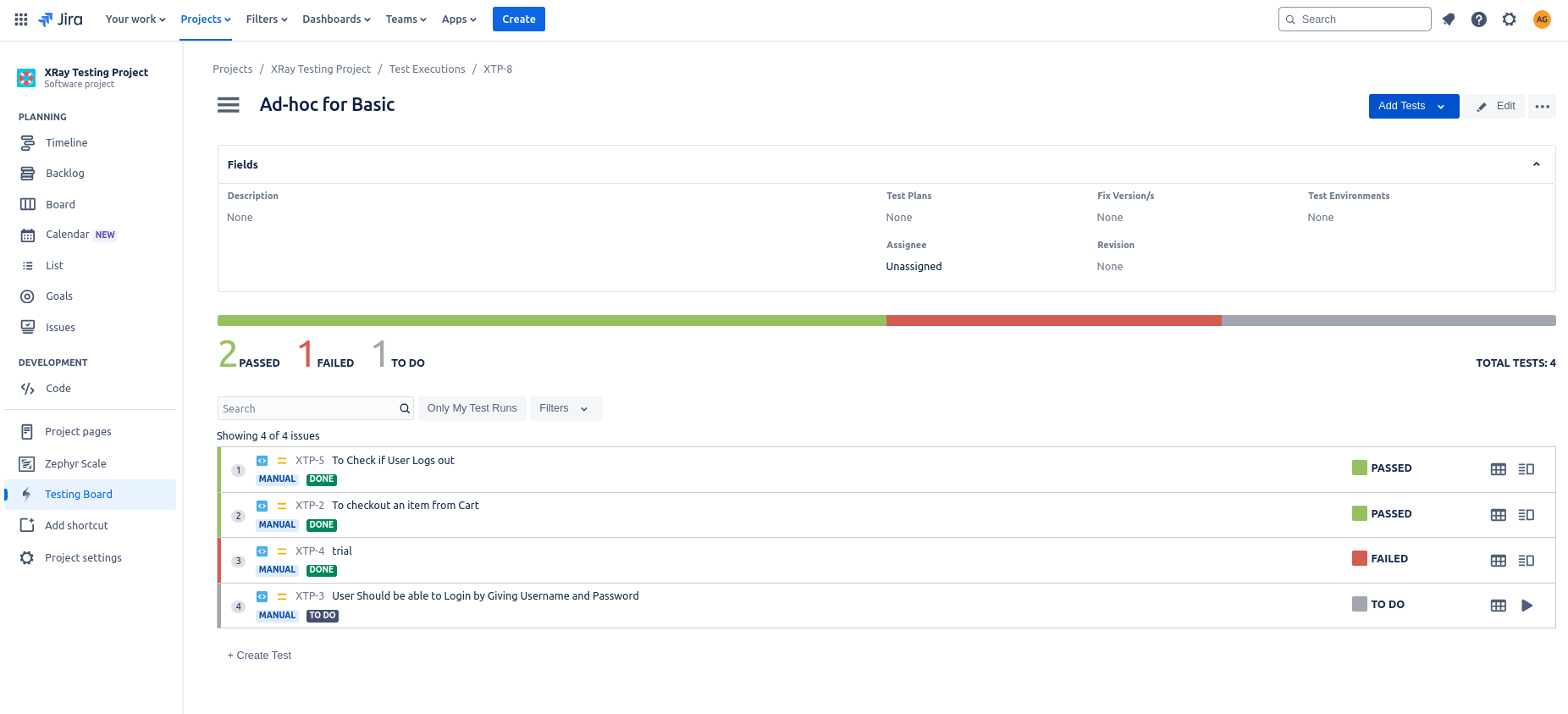
You can create Test Executions and add test cases to that. The test execution can be easily tracked with the overall progress with status of each test case executed.
Conclusion
Xray is a powerful test management tool. Its power lies in the seamless integration with Jira, which makes it easier for you to manage the testing activities within their existing workflows. It supports both manual and automated testing, providing a comprehensive solution for tracking test cases, planning test executions, and reporting on test progress and quality.
While it comes with some challenges, such as a learning curve and potential performance issues, the benefits of improved collaboration, enhanced traceability, and streamlined testing processes make it a valuable tool for many organizations.

