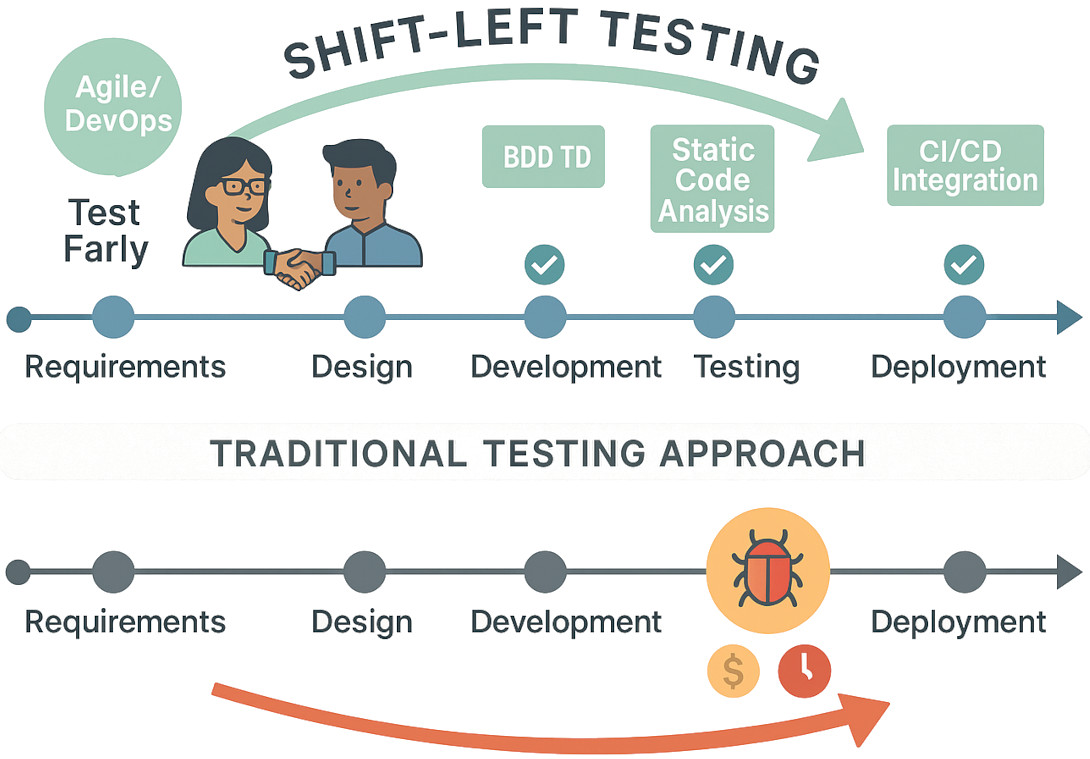
Speed and quality need to coexist peacefully in the fast-paced environment of software development. Quality assurance (QA), which takes place at the end stage of the development cycle in conventional testing models, often results in costly bugs, delayed deliveries, and decreased customer satisfaction. This is where the shift-left testing approach helps organizations in intensive QA practices. It is a methodology that prioritizes early and consistent testing.
However, what shift-left testing is, and why it is so critical in modern development methods such as DevOps and Agile, are questions we’ll seek answers to over here.
Understanding the Shift-Left Testing Approach
Shift-left testing entails the process of moving testing tasks to the initial stages of the software development lifecycle (SDLC). The conventional SDLC flowchart, which shifts from left(requirements and design) to right (development, testing, and deployment), is where the term “left” was first coined. Shifting to the left includes implementing QA early on, as compared to waiting until the code is finished.
As testing in conventional models is often initiated after development, bugs are detected later, when they are more expensive and time-consuming to resolve. Because developers and testers collaborate early on when leveraging the shift-left approach to testing, issues can be detected and fixed at a faster pace. According to a previous prediction by Gartner, shift-left testing would become a standard practice in more than 75% of enterprise DevOps initiatives.
Shift-Left Testing Principles
The core tenets of successful shift-left testing are proactive feedback, automation, and teamwork. The following are some fundamental principles:
- Early involvement of QA: To detect test scenarios early on, testers participate in design discussions and requirement analysis.
- Test-Driven Development (TDD): By building tests prior to code, developers can ensure they are focused on functionality right from the initial stages.
- Continuous Integration and Testing: Automated tests are executed after each code modification to rapidly identify regressions.
- Static Code Analysis: Pre-runtime identification of potential issues is made possible by automated tools that examine code quality without executing programs.
- Shift-Left Security Testing: As part of the DevSecOps philosophy, security validations initiate during development rather than waiting until after deployment.
Shift-Left Testing in Agile Environments
Agile methods rely on cross-functional cooperation and smaller, iterative development cycles. In this regard, Agile’s shift-left testing ensures that testing is embedded into each sprint.
Agile teams utilize a “test early and often” method in place of a unique QA phase. Along with features, automated test cases are developed, and user stories are written with acceptance criteria. By reducing the feedback loop, teams are able to deliver dependable software at a faster pace.
By ensuring that test design is a high priority in the process, agile also encourages behavior-driven development (BDD) and test-driven development (TDD), two methodologies that align perfectly with the shift-left philosophy.
Shift-Left Testing in DevOps
Automation, reliability, and speed are essential in DevOps. Teams can blend continuous testing into continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD) pipelines with the help of shift-left testing in DevOps.
Teams can detect flaws as soon as they are observed because every code commit is automatically tested. In dynamic DevOps settings, where deployments may occur multiple times a day, this is especially critical.
In DevOps, shift-left techniques often include:
- Automated unit and integration testing
- Performance testing while development is underway
- Static security scans
- Infrastructure-as-a-code validation.
When included in the right manner, these initiatives reduce deployment risks and promote reliable, high-quality releases.
Benefits of the Shift-Left Testing
For development teams and organizations, the shift-left testing method provides multiple benefits:
- Faster Feedback: Issues are identified by teams earlier, which aids their resolution.
- Reduced Costs: Bug fixes made during development are far less costly than those made during production.
- Improved Cooperation: Right from the start, developers and testers collaborate, promoting a sense of shared accountability for quality.
- Optimized Test Coverage: Frequent testing ensures more thorough and uniform verification across settings.
- Increased Agility: Accelerated innovation is possible without compromising quality through automated testing and faster iterations.
These advantages highlight why shift-left testing is a critical stage of successful DevOps and Agile adoptions.
Best Practices for Shift-Left Testing
Consider setting up and following the best practices below to get the most out of shift-left testing:
- Adopt a well-researched and planned method to validate automation: Prioritize stable and iterative tests, such as regression, unit, and smoke tests.
- Utilize the Relevant Tools: The right tool is essential for guaranteeing wide and efficient coverage. There are multitudes of tools available in the market. Selecting the right tool for your organization requires research. For instance, in the case of functional and UI testing, leverage Cypress, Selenium, Playwright, testRigor, etc. JMeter works well for performance testing. Similarly, TestRail works well for test management and SonarQube for static analysis.
- Ensure Cross-Layer Test Coverage: Incorporate unit, API, user interface, performance, and integration tests across the pipeline.
- Encourage a Testing Mindset across the Team: Train product owners and developers to bring in quality right from the start.
- Explicitly Define the Acceptance Criteria: Clearly define “done-ness” early to aid with test development and to align expectations.
- Frequently Review and Refactor Tests: Completely avoid faulty tests and ensure that automation suites are dependable.
How to Implement Shift-Left Testing
Organizations that consider this strategy often worry about how to successfully implement shift-left testing. Here is an in-depth framework:
- Involve QA early: Allow testers to participate in requirement reviews, planning sessions, and sprint grooming.
- Test Automation: Use tools such as API, UI, unit and integration testing. Automation coverage can be improved with tools such as Playwright, testRigor, Selenium, Cypress, JMeter, etc.
- CI/CD Pipelines with Embedded Testing: To guarantee that ongoing feedback is possible, set up automated tests to be executed with each code push. Utilize tools like TestRail to integrate dashboards and test reporting.
- Train Developers to Test: Encourage developers to build and execute their own tests, like unit tests.
- Utilize Static and Dynamic Analysis: To detect code issues early, bring in tools like ESLint or SonarQube.
- Use Shift-Left Tools: Make use of tools such as feature flagging systems and test virtualization that are built for proactive testing and feedback.
Be cognizant that the main goal is to ensure continuous quality assurance from start to finish, not just early testing.
Real-World Applications: Shift-Left in High-Risk Industries
Software malfunctions can have severe consequences in sectors such as automobiles, aerospace, and healthcare. Prior to integrating hardware, organizations use simulation-based validation and shift-left software testing to identify issues.
During the initial stages of development, innovative technologies such as software-in-the-loop (SIL) testing and hardware-in-the-loop (HIL) testing replicate real-world scenarios. This ensures that the safety regulations are met and drastically reduces the expense of defect resolution.
Hurdles and Considerations
Shift-left testing has multiple benefits, but it has its own set of disadvantages as well:
- Cultural Resistance: Teams familiar and comfortable with isolated development might resist changes in the methodology.
- Complex Tooling: Technical expertise is mandatory to integrate the right testing tools.
- Skill Gaps: Developers and testers are required to increase their knowledge of teamwork and automation.
- Risks due to Over-Automation: Prioritize tests as per the test stability and return on investment rather than automating the entire suite.
Organizations must encourage a culture of shared quality ownership and consistent learning in order to conquer these hurdles.
Why Shift-Left Testing Matters in Modern SDLC
Early, consistent, and collaborative testing is vital as software gets more complicated and delivery schedules shorten. Teams are facilitated to blend in quality into software from the start by incorporating the shift-left methodology.
Shift-left testing ensures that bugs are detected when they are less costly and software is produced with confidence, irrespective of whether you’re leveraging DevOps pipelines or working in an Agile sprint.
Organizations can accomplish a shortened time to market, improved products, and happier customers by embracing this strategy, which is grounded in teamwork, early testing, and automation.
